A more synergistic way to treat symptoms of hormonal imbalances.

The Importance of Hormones
Hormones have an intricate way of affecting a variety of physiological processes in the body. A proper balance of hormone and adrenal levels is vital for maintaining optimal health and well-being. When hormones are in harmony, they help regulate a wide range of bodily functions, including metabolism, growth and development, sexual function, mood, sleep, appetite, heart rate, and temperature regulation.
How Are These Functions Influenced by Hormones?

- Metabolism: Hormones like insulin, produced by the pancreas, regulate blood sugar levels and metabolism. Thyroid hormones also play a significant role in metabolism regulation.
- Growth and Development: Growth hormone, produced by the pituitary gland, is essential for growth during childhood and adolescence. Sex hormones also influence growth and development, particularly during puberty.
- Sexual Function: Sex hormones, including estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone, regulate sexual development and function. They influence characteristics such as libido, fertility, and secondary sexual characteristics.
- Sleep: Melatonin, produced by the pineal gland, helps regulate the sleep-wake cycle. It is involved in signaling the body when it’s time to sleep and when to wake up.
- Emotions and Mood: Hormones such as serotonin, dopamine, and oxytocin play roles in regulating mood and emotions. Imbalances in these hormones can contribute to mood disorders like depression and anxiety.
- Appetite: Hormones like ghrelin and leptin regulate appetite and feelings of hunger and satiety. Ghrelin stimulates appetite, while leptin signals fullness.
- Heart Rate: Hormones like adrenaline (epinephrine) and noradrenaline (norepinephrine), produced by the adrenal glands, increase heart rate and blood pressure in response to stress or danger.
- Body Temperature Regulation: Thyroid hormones help regulate body temperature by influencing metabolic rate. Additionally, adrenaline can increase body temperature as part of the body’s stress response.
Hormone Imbalance and How It Affects Us
Imbalances in hormone levels can lead to a variety of symptoms and health issues, impacting physical, emotional, and mental well-being. Addressing hormonal imbalances through approaches like lifestyle changes, medication, or hormone replacement therapy can help restore balance and alleviate symptoms, promoting overall health and quality of life.
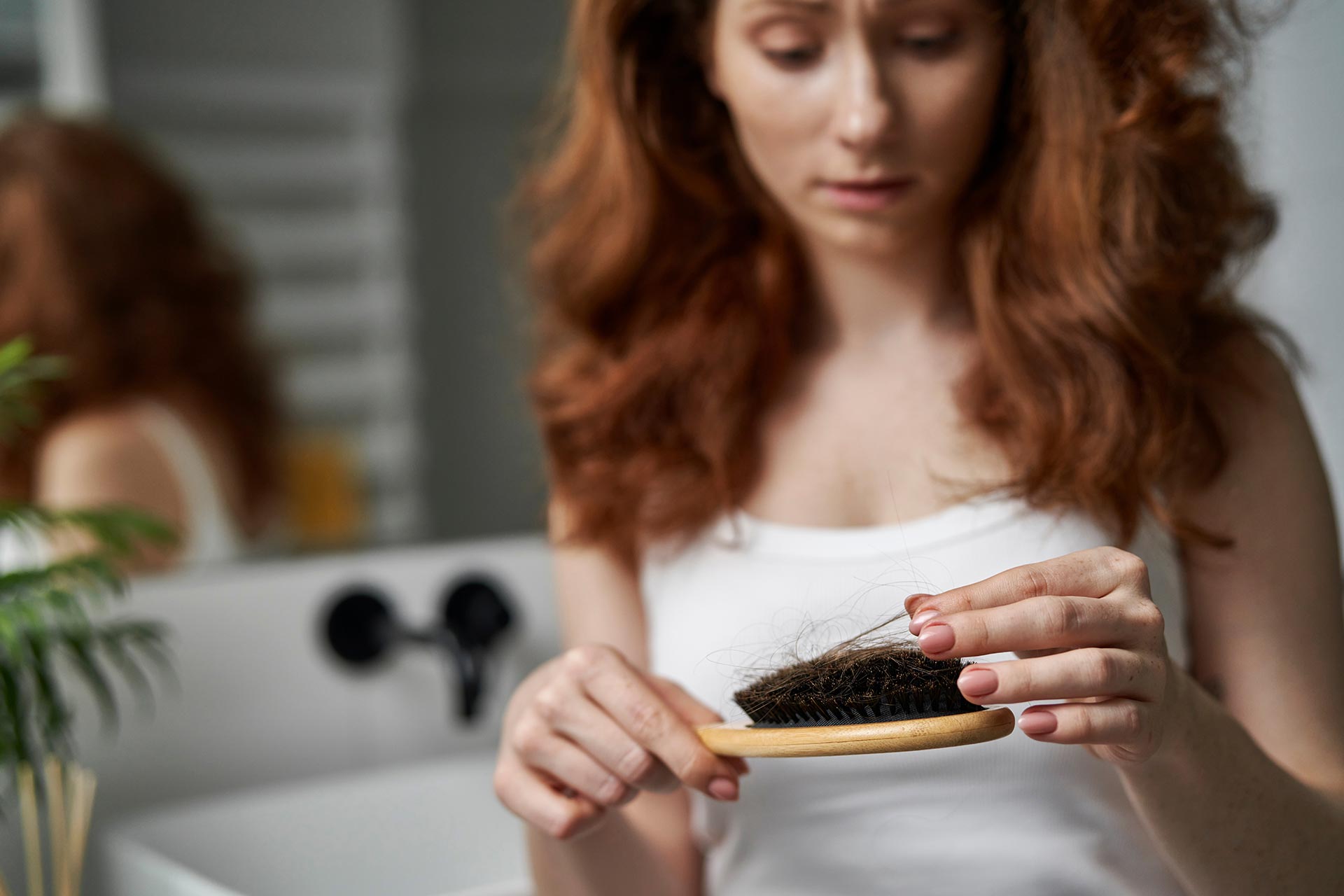

- Weight Gain: Hormonal imbalances, especially those involving insulin, thyroid hormones, and cortisol, can contribute to weight gain or difficulty losing weight.
- Mood Swings: Fluctuations in hormones like estrogen, progesterone, testosterone, and cortisol can lead to mood swings, irritability, anxiety, or depression.
- Low Sex Drive and Erectile Dysfunction: Changes in sex hormone levels, especially testosterone in men and estrogen in women, can affect libido and sexual function.
- Fatigue: Hormonal imbalances, especially involving thyroid hormones and adrenal hormones like cortisol, can cause fatigue, low energy levels, and difficulty concentrating.
- Insomnia and Difficulty Sleeping: Hormonal fluctuations, effecting melatonin levels, can disrupt sleep patterns and lead to insomnia or difficulty staying asleep.
- Hair Loss and Hair Thinning: Changes in hormone levels, particularly fluctuations in thyroid hormones and sex hormones, can contribute to hair loss or thinning.
- Hot Flashes and Night Sweats: Hormonal changes, often noted during menopause or perimenopause, can cause hot flashes and night sweats due to fluctuations in estrogen levels.
- Menstrual Irregularities: Hormonal imbalances involving estrogen and progesterone can lead to irregular menstrual cycles, heavy or light periods, or skipped periods.
- Depression: Hormonal fluctuations, primarily in estrogen, progesterone, testosterone, and cortisol levels, can contribute to feelings of depression or mood disturbances.
- Headaches or Migraines: Changes in hormone levels, reflected in fluctuations in estrogen and progesterone, can trigger headaches or migraines in some individuals.
Maintaining hormonal balance requires a holistic approach, including proper nutrition, regular exercise, stress management, adequate sleep, and seeking medical advice when necessary. By prioritizing hormonal health, individuals can optimize their overall well-being and enjoy a higher quality of life.
If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider for a proper evaluation and diagnosis. They can perform tests to assess your hormone levels and determine the underlying cause of your symptoms. Treatment options, including hormone replacement therapy or other interventions, can then be tailored to your specific needs.
Finding a Treatment that Fits
There is no “one size fits all” when it comes to balancing hormones and adrenals. To date, hormone therapy is still considered the most effective treatment for menopausal symptoms like hot flashes, insomnia, night sweats, and vaginal dryness. The FDA-approved synthetic estrogen-progestin hormone drugs have been shown to increase the risk of cancer and cardiovascular disease. Patients have also expressed resistance in taking traditional drugs for the cascade of hormone symptoms when they are geared at treating menopause as a disease rather than a normal stage of life.
To adapt to the need for a more natural option – “bioidentical” hormone therapy (BHRT), a more synergistic way to treat symptoms of hormonal imbalances. Hormone replacement therapy (BHRT) is a specialized treatment that requires individualized care and monitoring.

Personalized Treatment
Hormone levels and needs vary greatly from person to person. What works for one individual may not work for another. Therefore, BHRT needs to be tailored to each person’s specific hormone levels, symptoms, and medical history.
Regular Monitoring
Hormone levels can fluctuate over time, and the effectiveness of BHRT may change accordingly. Regular monitoring through blood tests and clinical evaluations is essential to ensure that hormone levels are optimized and that any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan can be made.
Minimizing Risks
Hormone levels and needs vary greatly from person to person. What works for one individual may not work for another. Therefore, BHRT needs to be tailored to each person’s specific hormone levels, symptoms, and medical history.
Optimizing Symptom Relief
The goal of BHRT is to alleviate symptoms associated with hormone imbalances, such as hot flashes, mood swings, and fatigue. Regular check-ups allow healthcare providers to assess the effectiveness of treatment and make adjustments as needed to ensure optimal symptom relief.
Long-Term Health
Hormone imbalances can have long-term implications for overall health and well-being. By closely monitoring hormone levels and adjusting treatment as necessary, healthcare providers can help promote long-term health and reduce the risk of complications associated with hormone imbalances.
Overall, regular visits to your doctor’s office are crucial for ensuring that hormone replacement therapy is safe, effective, and tailored to your individual needs. Your healthcare provider will work with you to optimize your hormone levels and improve your quality of life.

We are a certified BioTE provider
BioTE offers a revolutionary approach to hormone balance, providing relief and rejuvenation for both men and women.
With personalized pellet therapy, BioTE optimizes hormone levels to enhance overall health and vitality. Say goodbye to age-related symptoms and hello to renewed energy, mental clarity, and happiness. Experience the difference of BioTE and reclaim your well-being today!
Other Services

IV Therapy
Aesthetics